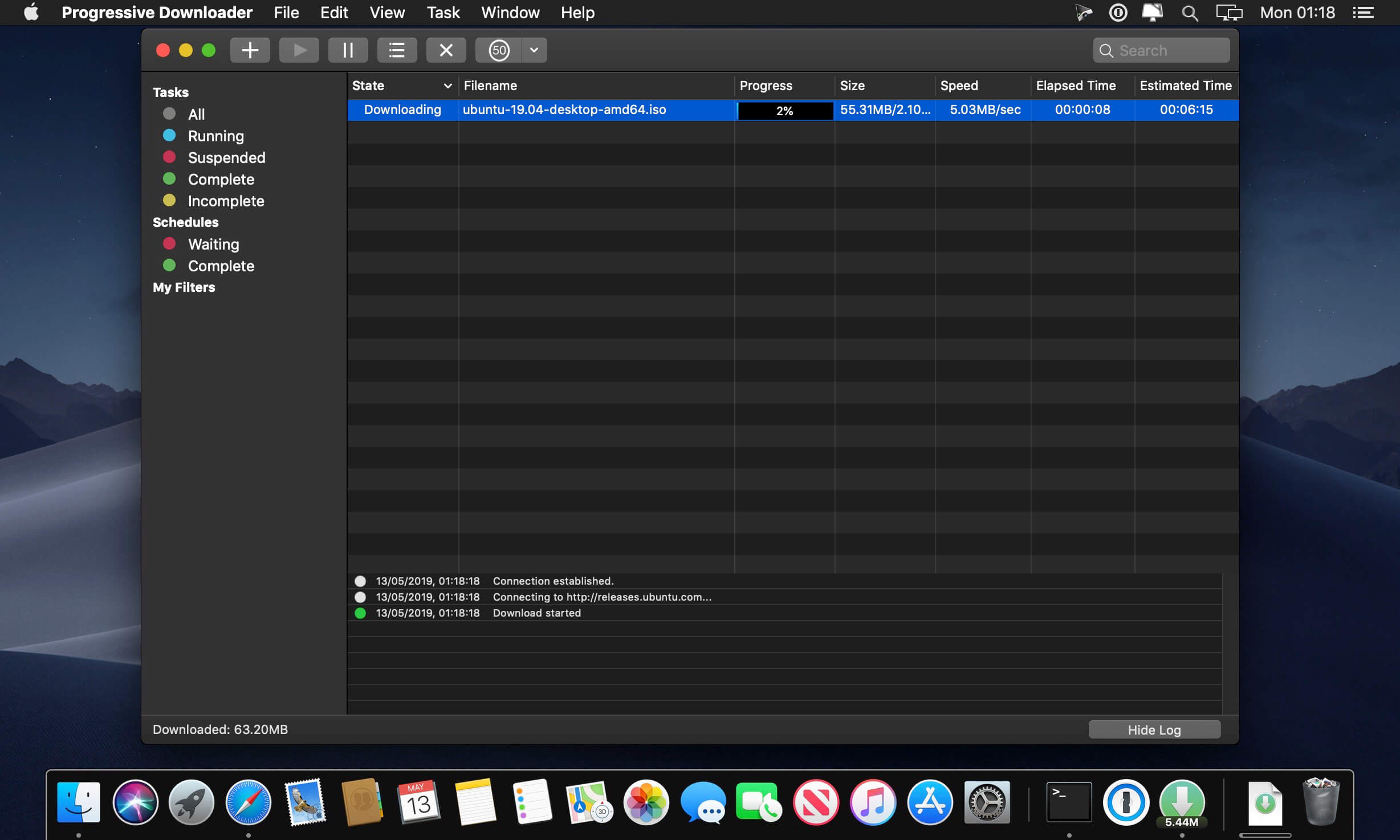
Progressive download means that a video file is a monolithic block on the server and the browser asks the server for that file. The browser may not fetch the whole file, it probably asks for a byte range so that it can play back a segment then fet. Progressive download describes the download process of digital media files, which allows a user to access a file's contents before the download has been completed. The end user's experience is very similar to that provided by streaming media, and the fact that the full file has not been downloaded is often unnoticeable. For slower connections.
| In order to integrate Progressive Downloader with your favorite browser you need to install the Interceptor. Allow browser to launch Progressive Downloader if you're asked. |
Switch to Progressive Downloader and select the Interceptor preferences from the main menu of the application. In case you don't see the menu item, please perform installation again.
If you purchased a printed book, we will then ship it to you. If you purchased an ONLINE product like DAILY SHEETS, SELECTIONS or a DERBY ZONE, then click on ACCESS DOWNLOADS. BC BASH 2016 PICK 6 CARTEL CASHES OUT FOR $292K + consolations. The 14-player cartel went 4 and 5 deep in five legs and used California Chrome and Arrogate in the Classic.
Click Install to start the integration procedure.
Wait until the Interceptor finds all supported browsers on your mac and select the browser you want to integrate with. At the very moment the Interceptor is compatible with:
- Apple Safari
- Mozilla Firefox
- Google Chrome
- Chromium
- Opera Internet Browser (based on Chromium)
- Yandex Browser
- SeaMonkey
- Beta versions of the browsers listed above
Select types of files you wish to download in Progressive Downloader and click Finish.
The last step is to install extension to your browser.
Since version 2.2, Progressive Downloader is capable to use cookies of the browser the application is integrated with. Mi note 5 pro wallpaper 4k. In other words, you only need to login to a private section of some web-site in your browser to be able to download files from the section in Progressive Downloader.
Note! Starting macOS Mojave access to Apple Safari's cookie database is forbidden by default. See how to grant Progressive Downloader access.
Watch a short video below to see an example:
You can forbid the application to use browser's cookie storage anytime you want by unchecking the appropriate box on the Integration tab.
If you ever want to integrate Progressive Downloader with two or more of your browsers you need to do the following. For example, you have Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari and Google Chrome. Start with Mozilla Firefox and then go back to the Interceptor's preferences window to click Delete. Don't be afraid, you will loose nothing. After your click the Delete button turns to the Install button. Click it and go through the integration process again with Apple Safari. Switch back to the preferences window and click Delete once more to finish the whole thing up with Google Chrome.
The trick is that you need always start with the Mozilla browsers before switch to all the rest. Iffmpeg 6 1 11 – convert multimedia files between formats.
Keep in mind that Progressive Downloader will use the cookie storage of the last browser you integrated with. Word docx converter mac. Online webpage creator.
A progressive download is the transfer of digital media files from a server to a client, typically using the HTTPprotocol when initiated from a computer. The consumer may begin playback of the media before the download is complete. The key difference between streaming media and progressive download is in how the digital media data is received and stored by the end user device that is accessing the digital media.
A media player that is capable of progressive download playback relies on meta data located in the header of the file to be intact and a local buffer of the digital media file as it is downloaded from a web server. At the point in which a specified amount of data becomes available to the local playback device, the media will begin to play. This specified amount of buffer is embedded into the file by the producer of the content in the encoder settings and is reinforced by additional buffer settings imposed by the media player.
History[edit]
Progressive Downloader Windows
Initially the digital media file type known as JPEG was the first visual media to render a progressive visual display as the digital media was downloaded and actually referred to as a progressive download. The distinction between the technical behavior of progressive download as opposed to the common or commercial use of the term progressive download to describe that behavior was not documented and there is a good deal of question regarding the origin of the term versus the origin of the technical implementation. Apple in reference to their QuickTime media player employed the term Fast Start[1] in 1997, to describe what was commercially referred to as progressive download playback of encodeddigital media content.
HTTP progressive download versus streaming media[edit]
The end user experience is similar to streaming media, however the file is downloaded to a physical drive on the end user's device; the file is typically stored in the temporary directory of the associated web browser if the medium was embedded into a web page or is diverted to a storage directory that is set in the preferences of the media player used for playback. The file will stutter or stop playback if the rate of playback exceeds the rate at which the file is downloaded. The file will begin to play again after further download.
This fast start playback is the result of moving the meta data from the end of the digital media file to the front, this move of the meta data gave the media player all the information it required to begin playback as the file was still being downloaded. Prior to that change, the meta data summary was located at the end of a media file and the entire file would need to be downloaded in order for the meta data to be read and the player begin playback.[2]
Seeking[edit]
Initially, the file is played from the beginning. A user may wish to point to a part of the file which haven't been downloaded yet. This capability is called seeking[3] and it makes possible to download and start playing any part of the media file. That is often referred to as pseudo-streaming.
For Flash video seeking requires a list of seek points in the media file metadata. These points are offsets in the video (both in seconds and bytes) at which a new key frame starts. A web server or a media server which handles the download, must support seek points in query string of requests for downloading data.
https://coollload220.weebly.com/fxfactory-pro-7-1-7-8.html. For other types of media files such as MP4 or MKV, web servers must be capable of handling a special offset parameter. The offset parameter name differs for various servers so it must be specified in player settings.
Some servers support seeking via additional modules only, they are specified below. Seeking parameter names are written in italic.
Progressive Downloader Mac
| Server | Flash seeking | MP4 seeking |
|---|---|---|
| Apache HTTP Server | mod_h264start mod_flvxstart | mod_h264starttime |
| lighttpd | start | mod_h264starttime |
| Nginx | http_flv_modulestart | http_mp4_modulestart |
| Nimble Streamer | start | start |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^QuickTime Streaming Server 4.1(PDF), archived from the original(PDF) on 2011-07-06, retrieved 2010-09-21,
Two methods are commonly used to deliver media over the web for real-time viewing: progressive download (Fast Start) and real-time streaming.
- ^Understanding the MPEG-4 movie atom, retrieved 2015-07-17
- ^Pseudo Streaming in Flash, retrieved 2015-07-17
External links[edit]
- Streaming vs Progressive Download, archived from the original on 2010-08-18
- Web Server vs. Streaming Server, Microsoft, retrieved 2010-09-21
- Flash Video: Progressive Download, retrieved 2010-09-21
- Video Streaming Vs Progressive Download, archived from the original on 2015-05-29, retrieved 2015-05-29
| Server | Flash seeking | MP4 seeking |
|---|---|---|
| Apache HTTP Server | mod_h264start mod_flvxstart | mod_h264starttime |
| lighttpd | start | mod_h264starttime |
| Nginx | http_flv_modulestart | http_mp4_modulestart |
| Nimble Streamer | start | start |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^QuickTime Streaming Server 4.1(PDF), archived from the original(PDF) on 2011-07-06, retrieved 2010-09-21,
Two methods are commonly used to deliver media over the web for real-time viewing: progressive download (Fast Start) and real-time streaming.
- ^Understanding the MPEG-4 movie atom, retrieved 2015-07-17
- ^Pseudo Streaming in Flash, retrieved 2015-07-17
External links[edit]
- Streaming vs Progressive Download, archived from the original on 2010-08-18
- Web Server vs. Streaming Server, Microsoft, retrieved 2010-09-21
- Flash Video: Progressive Download, retrieved 2010-09-21
- Video Streaming Vs Progressive Download, archived from the original on 2015-05-29, retrieved 2015-05-29
